JUPYTER NOTEBOOK SHORTCUTS AND MOST USED CODE SNIPPETS FOR BEGINNERS
I have summarized the Jupyter Notebook shortcuts and the most used code snippets below that will save your time while using Jupyter notebook.
Shortcuts
These shortcuts are for Jupyter Notebook version 5.6.0.
Command mode and Edit mode
When using shortcuts, it is necessary to pay attention to whether the notebook is command or editing mode.
1. Command mode:
2. Edit mode:
Command Mode
- shift + enter executes cell and selects the cell below.
- ctrl + enter executes cell.
- alt + enter executes cell, adds a cell below the selected cell and tab is active in.
- A adds a cell above the selected cell.
- B adds a cell below the selected cell.
- C copies cell.
- V paste cell.
- D , Pressing D 2 times deletes the selected cell.
- shift + M Hold down shift, select cells, and then press M, cells are merged.
- I , If I is pressed 2 times consecutively, the kernel stops.
- 0 , Restarts the kernel with the dialog box.
- Y , returns the cell to code mode.
- M, returns the cell to markdown mode.
Edit Mode
- ctrl + click Multiple editing can be done by holding down ctrl and selecting multiple cursors with the mouse.
- ctrl + / If ctrl is pressed and the lines to be commented are selected “/” pressed, collective comments are made.
- tab to complete and indent code
NOTE : cmd +shift + p You can list all commands in Jupyter Notebook.
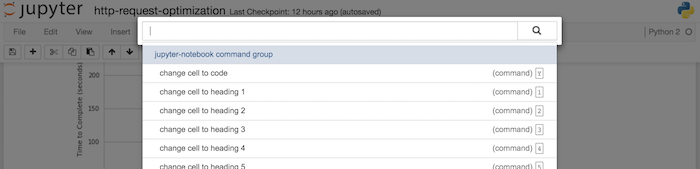
View all keyboard shortcuts
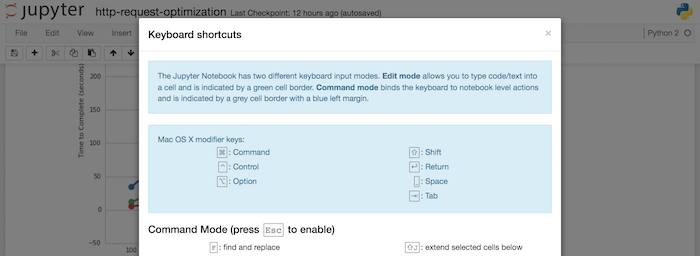
If you press H ‘(in Command Mode), you can see what are the shortcuts on the keyboard.
Text snippets
Below are the text snippets you will use frequently while working on the notebook.
from __future__ import division
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
from numpy.random import randn
from scipy import stats
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_style('whitegrid')
%matplotlib inline
import math
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
import statsmodels.api as sm
from pprint import pprint
Sources: